Publications
Across these areas, my work treats application domains as diagnostic tools for studying representation learning, rather than as ends in themselves.
Semantic Segmentation
My work in semantic segmentation explores how principles from visual perception and physical image formation can be embedded into deep learning architectures to improve robustness and generalisation in complex real-world conditions. I use visually challenging data to expose systematic model weaknesses and to motivate more principled architectural design. By incorporating perceptually grounded and physically informed inductive biases, my work develops representations that are more stable under occlusions, illumination changes, and domain shifts, while also improving interpretability.
Georgios Voulgaris. (2025). “Bridging Classical and Modern Computer Vision: PerceptiveNet for Tree Crown Semantic Segmentation.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) EarthVision. Full text available at CVPR’25 . Spotlight
Georgios Voulgaris, Andy Philippides, Novi Quadrianto. (2023). “Water Physics Aware Semantic Segmentation Through Texture-Biased U-Net Architectures.” International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). Full text available at IGARSS’23 . Oral
Multimodal Deep Learning Data Fusion
My work in multimodal learning investigates how the physical properties of different sensing modalities can serve as inductive biases for representation learning. By incorporating perceptually grounded and physically informed inductive biases, my work develops representations that leverage complementary signals to expose persistent physical structure often obscured by single-modality or direct cues. These ideas are validated on real-world multi-spectral and thermal datasets, demonstrating improved generalisation and interpretability in complex environmental settings.
Georgios Voulgaris. (2026). “FusionNet: Physics-Aware Representation Learning for Multi-Spectral and Thermal Data via Trainable Signal-Processing Priors.” IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing (JSTARS), under review.
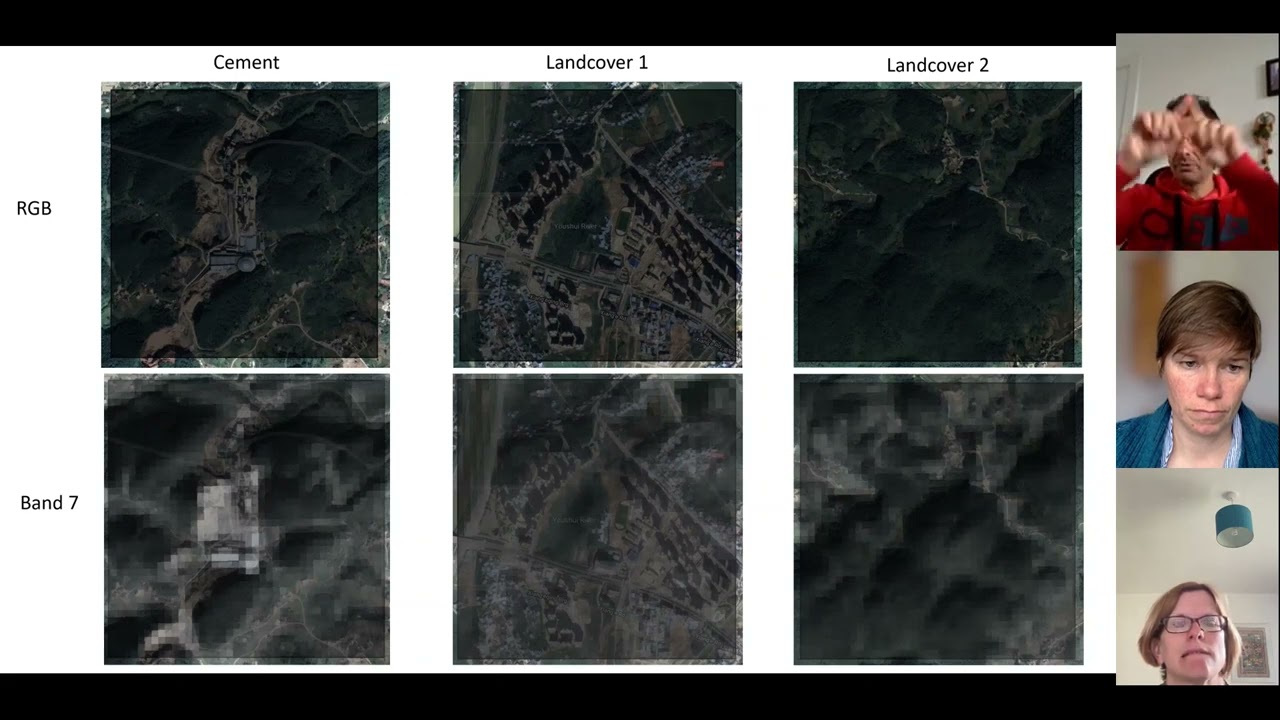
Georgios Voulgaris, Maral Bayaraa, Cristian Rossi. (2025). “Detecting Cement Plants with Landsat-8: A Physics-Informed, Multi-Temporal, and Multi-Spectral Deep Learning Fusion Approach.” International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). Full text available at IGARSS’25 . Oral
Cristian Rossi, Nataliya Tkachenko, Maral Bayaraa, Peter Foster, Steven Reece, Kimberly Scott, Georgios Voulgaris, Christophe Christiaen, Matthew McCarten. (2022). “Detection and Characterisation of Pollutant Assets with AI and EO to Prioritise Green Investments: The Geoasset Framework.” International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). Full text available at IGARSS’22. Oral
Domain Adaptation
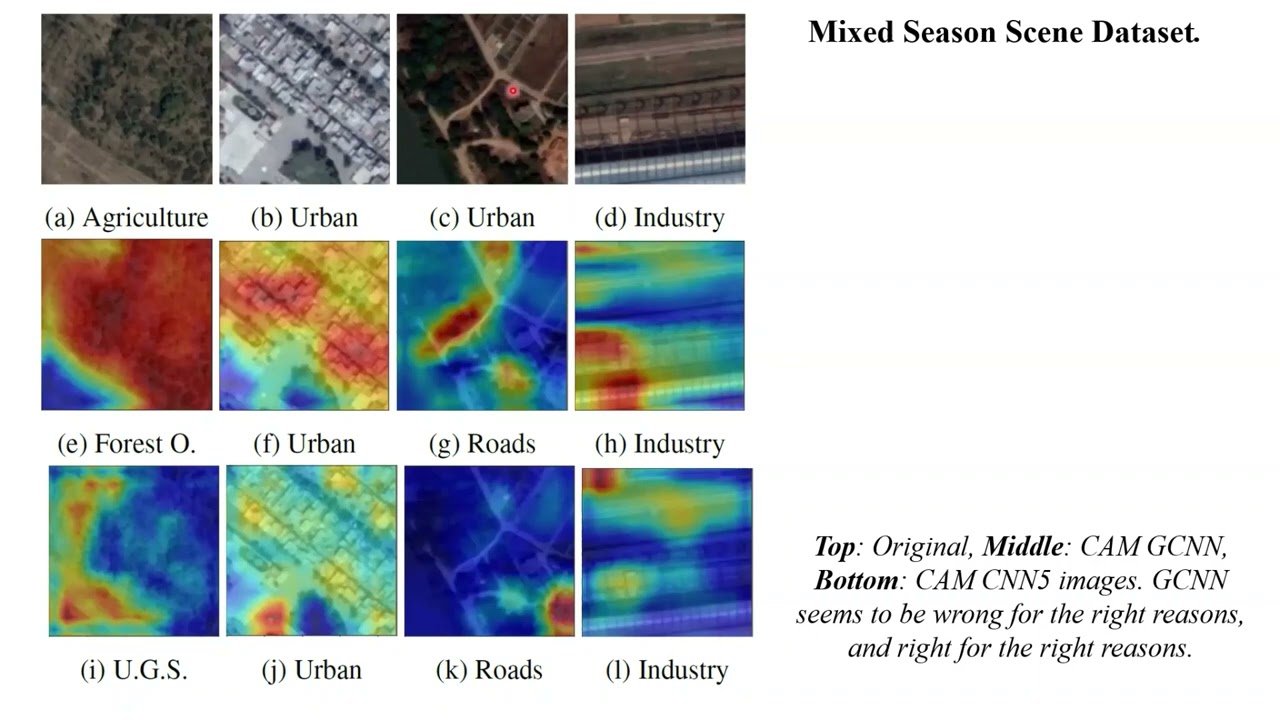
My work in domain adaptation investigates how seasonal and environmental variation creates systematic domain gaps, and how perceptually grounded and physically informed inductive biases can produce more domain-invariant representations. I use seasonal shifts as a stress test to expose colour- and texture-biased failure modes and to motivate architectural designs that emphasise persistent, physically meaningful structure over spurious appearance cues. The resulting representations are more robust across seasons and more interpretable, particularly in visually complex outdoor environments.
- Georgios Voulgaris, Andy Philippides, Jonathan Dolley, Jeremy Reffin, Fiona Marshall, Novi Quadrianto. (2023). “Seasonal Domain Shift in the Global South: Dataset and Deep Features Analysis.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) EarthVision. Full text available at CVPR’23 .
- Georgios Voulgaris, Andy Philippides, Novi Quadrianto. (2022). “Deep Learning Robustness to Domain Shifts During Seasonal Variations.” International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). Full text available at IGARSS’22 .
PhD Thesis
This research explores transferable features between domains, proposes Deep Learning architectures that combine salient feature extraction with a wider receptive field and highlights the importance of choosing appropriate feature priors for better model generalisation for domain adaptation and semantic segmentation tasks.